|
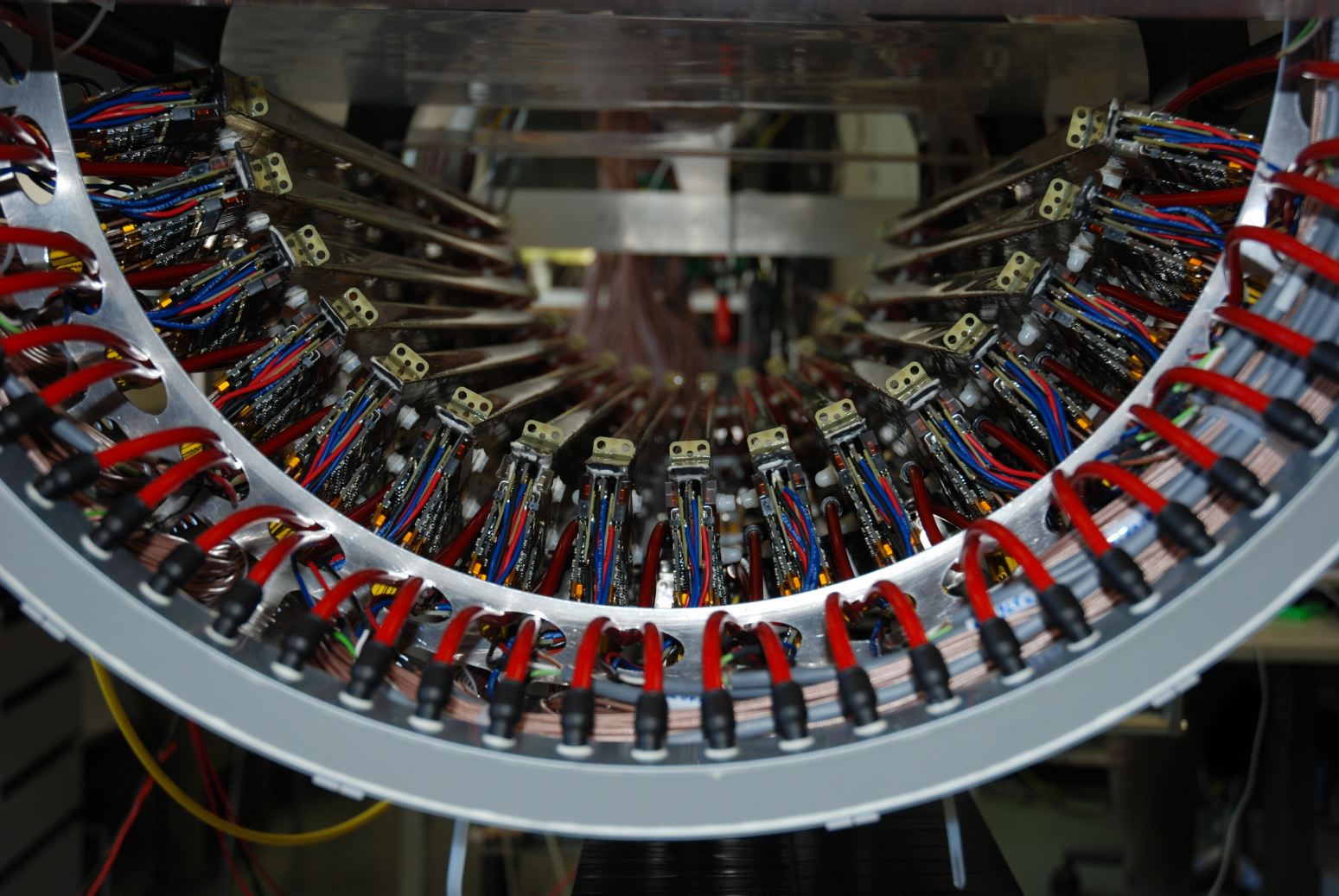
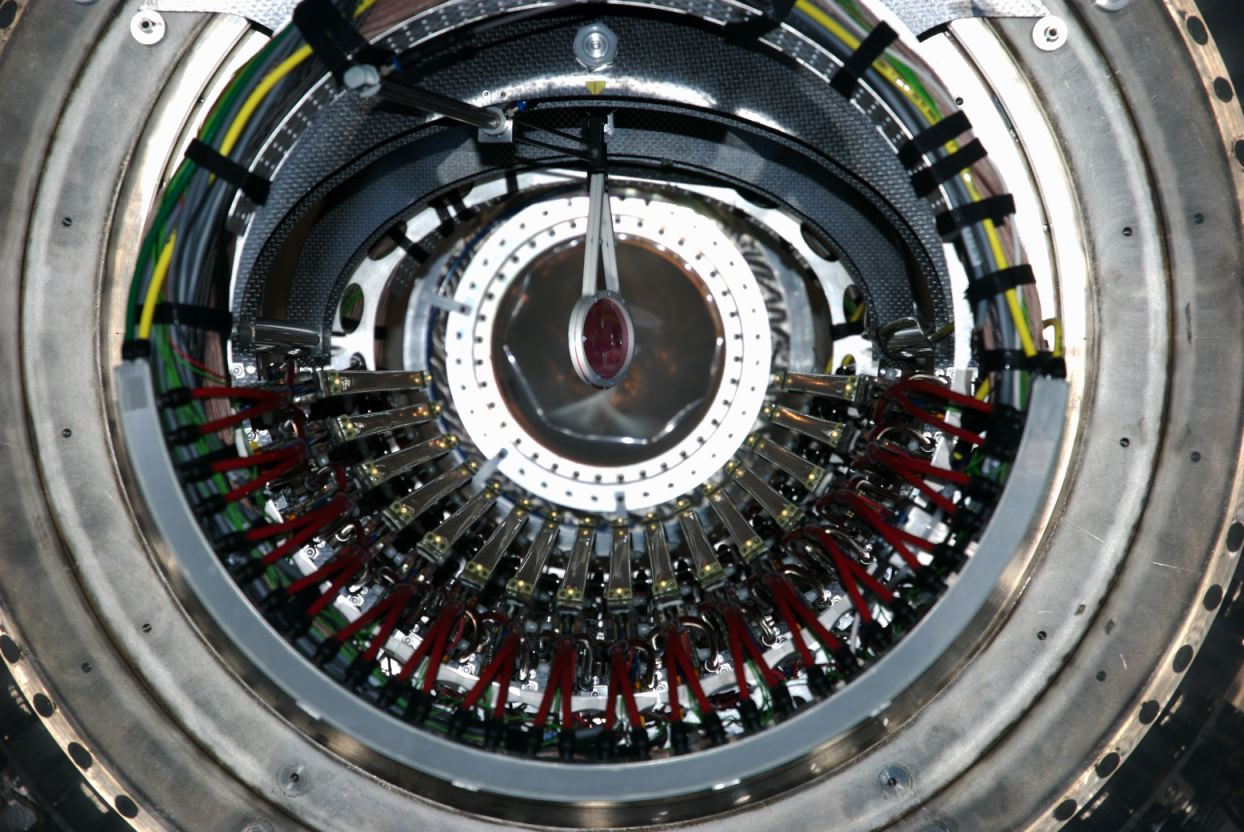
The MEG positron spectrometer consists 16 drift chambers as shown in
Fig 1. (only 6 sectors are shown to simplify view).
These are aligned radially at 10.5 ° intervals in azimuthal angle.
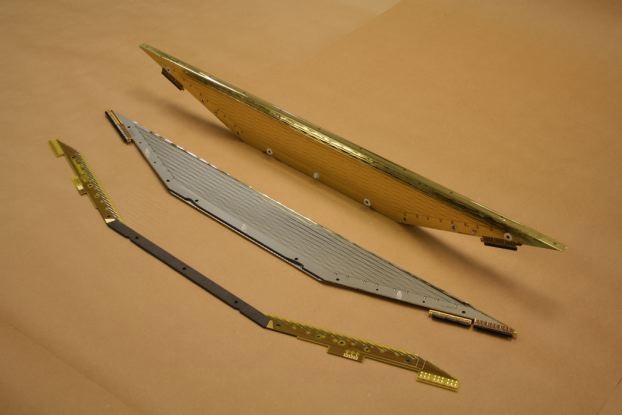
For the each DC module, two layers of axial sense wires and potential
wires stretched by a 4.5 mm pitch are formed on the carbon-fibre frame.
Each layer is isolated by a ultra-thin cathode foil,
described later, and shifted by one-half cell to allow a
local resolution of left-right ambiguity.
A schematic cross-sectional view of a part of single chamber module
is shown in Fig 2.
In order to reduce the amount of material used in the spectrometer,
a helium based gas mixture (50% helium and 50% ethane at 1 atm)
is adopted as a chamber gas.
Additionally, the gaps between each chamber module are filled with
pure helium gas.
The chamber wall is made of an extremely thin foil, 12.5 μm thick
polyimide with aluminum deposition (2500 Å).
The frame of drfit chamber is shaped without any structure on the
muon stopping target side.
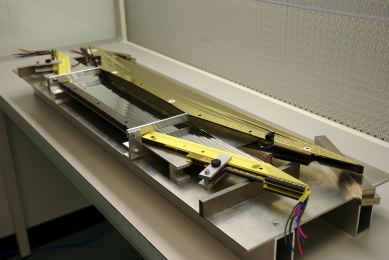
This opend-frame (see photo, Fig 3.) makes wire/foil-stretching
more challenging but helps very much.
Thanks to such an exhaustive reduction of material, the overall material
in the fiducial tracking volume amounts to 0.002 X0 on an
average for the signal positron (52.8MeV/c) trajectry.
The staggered-cell configuration allows us to measure the r-coodinate
and the absolute time of the track simultaneously. Difference between
the drift times (t1-t2) in the adjacent cells gives the r-coodinate of
the track with 200 μm accuracy,
while the mean time (t1+t2)/2 gives the absolute
time of the track with 5 nsec accuracy.
On the other hand, the ratio of charges collected at both ends of
a sense wire gives the z-coordinate (muon beam direction) roughly
with an accuracy of approximately 1cm.
Moreover, ultra-thin aluminum deposit on the cathode foil is patterned
to make a 5cm period Zig-Zag strip, called "vernier pad"
(Fig 4.).
The amount of induced positive charge on each vernier pad is related to the
z-coordinate because of this Zig-Zag shape.
Concequently, the ratio of charges induced on each pad gives
the z-coordinate precisely to an accuracy of 300∼500 μm.
|
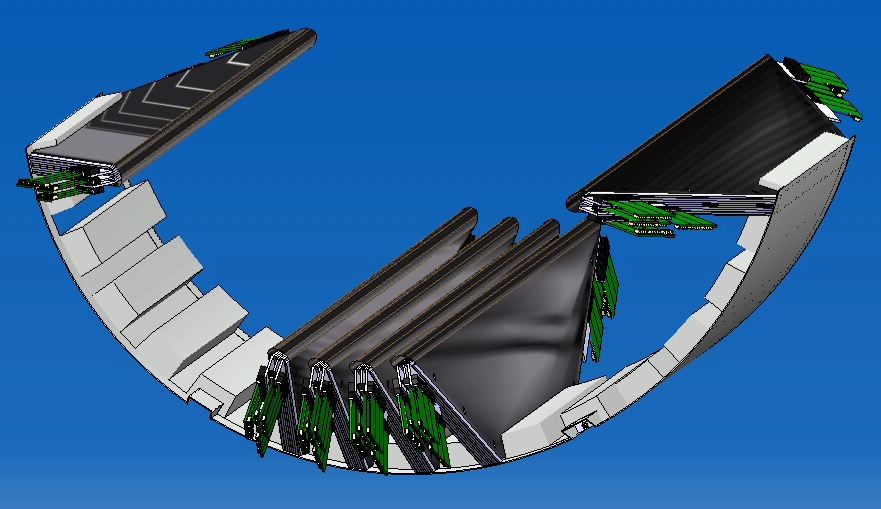
Fig 1. MEG DC Overview
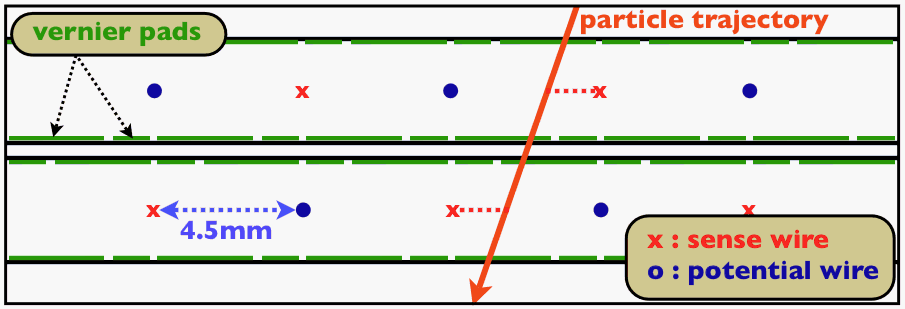
Fig 2. Cell configuration
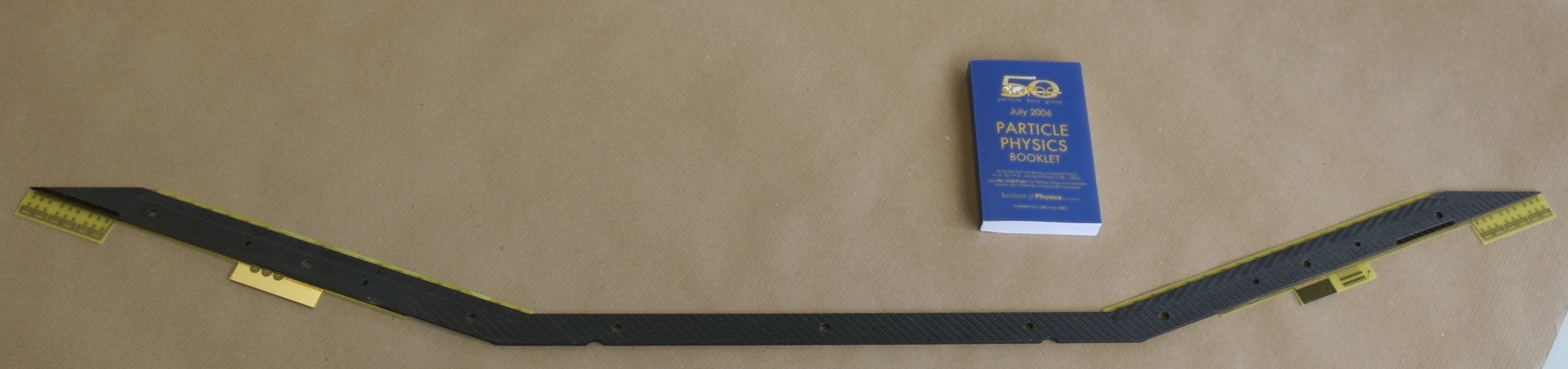

Fig 3. Opened anode frame
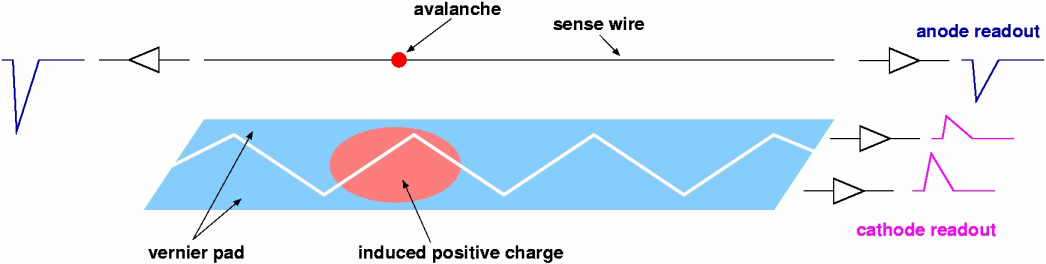
Fig 4. Schematic view of the vernier pad method
|